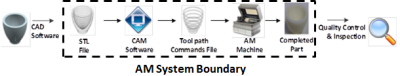
Fused Filament Fabrication

Material Extrusion operates in a similar fashion to a hot glue gun; plastic filament is heated to a malleable state and extruded through a nozzle. In order to create a part, a CAD model is sliced into layers. The nozzle uses g-code to draw each layer, one at a time, with the heated plastic, which then cools and transitions back into a solid state.
If the part has large overhangs, support material is required to prevent sagging and protect part integrity. This support material is created either through thin, breakable trusses of the build material or a second soluble material.
Material Extrusion of ABS allows for:
- Strong parts (Tensile strength of ABS is 5,000 psi)
- Material Extrusion ABS is machineable, sandable and paintable
- Can be treated with resins to strengthen the plastic and increase heat resistance
- Relatively cheap compared to other AM processes (~$250.00 per 56 in3 of material)
Our Systems
Stratasys Fortus 400mc
The Fortus 400mc is a larger version of the 250mc located in the DREAMS Lab. It offers the same properties as the 250mc, but can also print in ULTEM, a much stronger and durable plastic material.
AON 3D AON-M2 2020
Modern large-scale FFF platform capable of printing PEEK, ULTEM, and other high performance thermoplastics.
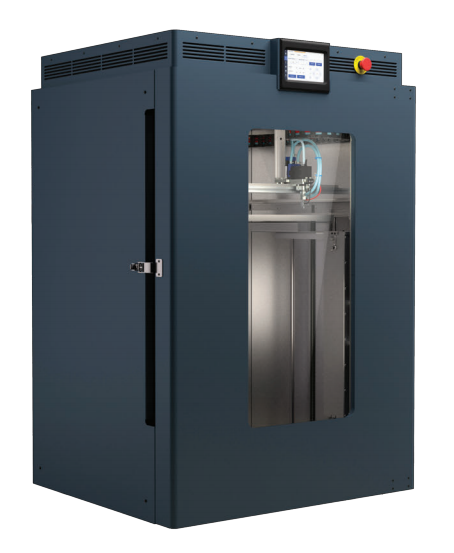

Rize One
(Custom-built) Desktop-scale High Temperature FFF
Desktop-scale FFF Systems
Desktop fabricators give individual users the ability to print their own part designs or those of others’ from websites like MakerBot Industries’ Thingiverse. These small-scale systems open the door for widespread personal use of additive manufacturing technologies.

Filabot EX2
Filabot EX2 is a desktop level filament extruder compatible with a wide range of polymer materials, and it allows you to convert both virgin or recycled plastic pellets into filament for different 3D printers. In addition, this machine can also be used in developing filaments from not commercialized new materials in research facilities.
Active Projects
-
General Item