Robotic Material Extrusion
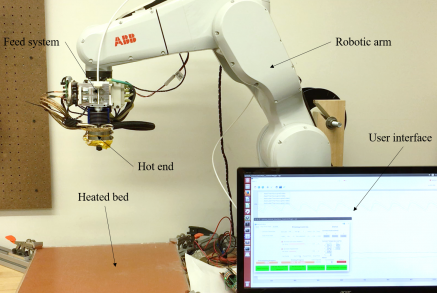
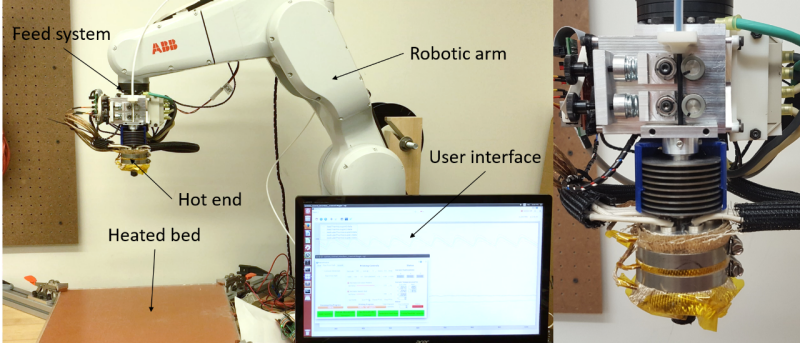
Project Overview
Goal:
Explore the possibilities of material extrusion by removing the constraints imposed by using a 3 degree of freedom (DOF) gantry.
Project Description:
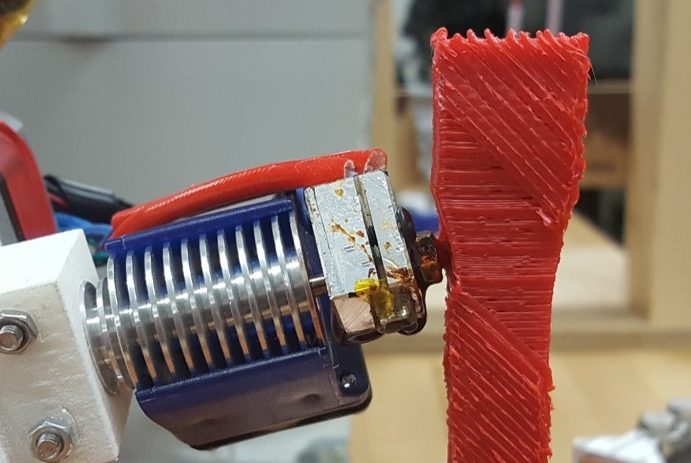
Material extrusion is a process by which material is precisely deposited onto a substrate layer by layer to create part geometry. This process has a number of limitations including the necessity of support material, surface artifacts, and anisotropic material properties. These all at least partially stem from the use of a 3 degree of freedom (DoF) gantry, which limits material deposition to take place only in the vertical axis. Adding additional DoF into the system allows reorientation of the tool head, resulting in the ability to deposit material off of the vertical axis. The robotic material extrusion platform focuses on the use of a 6-DoF industrial robotic arm and custom extrusion system.
Project History:
The project began as a senior design team from Fall 2015 to Spring 2016. A team of 7 mechanical engineering seniors took the provided robotic arm and built the system. This included development of the software architecture (ROS based), communication, and heated bed. Additionally, the team designed, modeled, and fabricated their own custom deposition head intended for processing high performance composite materials. The result of this project was able to print using full 6-DoF motion and gave a good starting point for future research. Since the senior design team, the system has gone through a number of iterations to make it more applicable to multi-axis deposition.
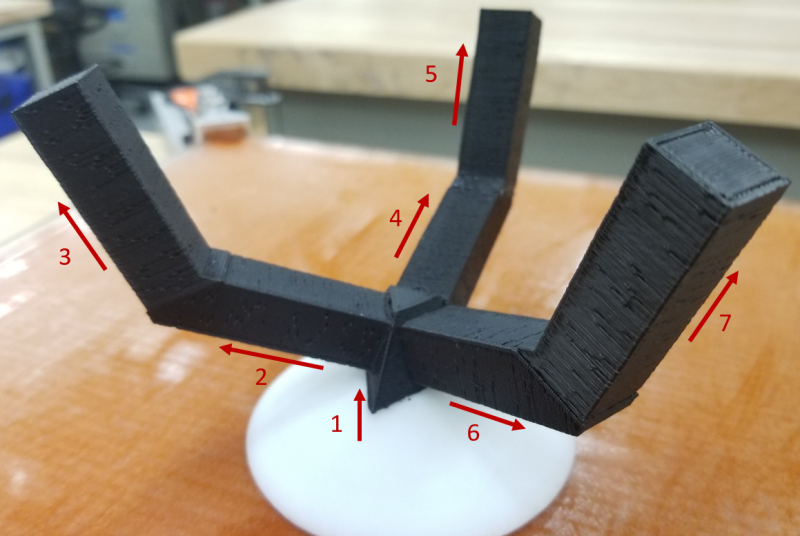
In Fall 2017, the multi-axis platform was exhibited at the Smithsonian National Museum of American History as part of the ACC Smithsonian Creativity and Innovation Festival. Here, the platform was fabricating a branched part with large overhangs, making use of the multi-axis capabilities to eliminate the need for support material. There are seven unique build directions in the part.
Research Projects:
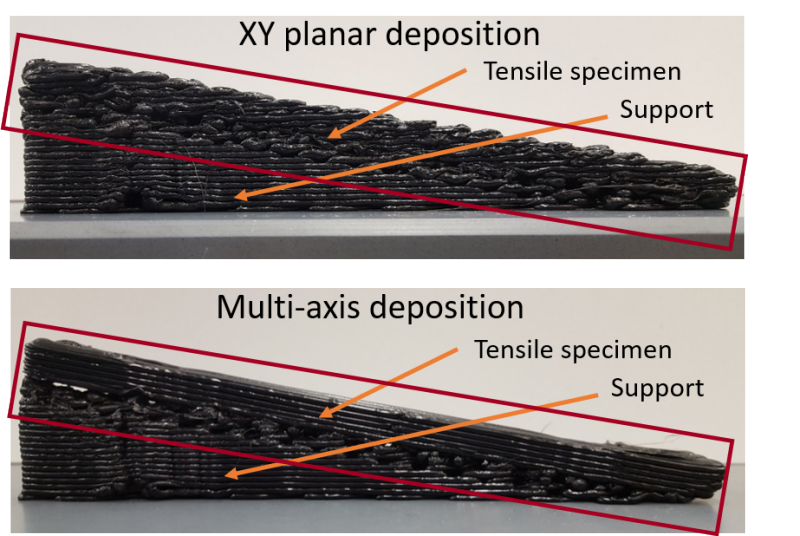
The muli-axis platform is used as a testbed for novel toolpath planning algorithms. The additional flexibility afforded by the 6-DoF arm enable local variations in deposition and layering directions. Whereas in 3-DoF printing, material could not follow load paths along the build direction, multi-axis printing enables deposition in any direction. This allows material to be used in a more efficient manner, as it can more effectively follow load paths.
Related Publications
- Kubalak, J. R., Mansfield, C. D., Pesek, T. H., Snow, Z. K., Cottiss, E. B., Ebeling-koning, O. D., … Wicks, A. L. (2016). Design and Realization of a 6 Degree of Freedom Robotic Extrusion Platform. Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, 1314–1332.
- Kubalak, J. R., Wicks, A. L., & Williams, C. B. (2017). Using multi-axis material extrusion to improve mechanical properties through surface reinforcement. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 1–7.
J. R. Kubalak, A. L. Wicks, C. B. Williams, “Deposition Path Planning for Material Extrusion using Specified Orientation Fields,” in 47th SME North American Manufacturing Research Conference, vol. 00, pp. 1-100, Elsevier, 2019
Related Presentations
- Kubalak, J. R., Wicks, A. L., Williams, C. B. (2017). Using Multi-Axis Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing to Improve Part Mechanical Properties through Printed Surface Reinforcement. Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium.
- Kubalak, J. R. & Williams, C. B. (2018). “Robotic Deposition to Enable Multi-Axis Material Extrusion,” in TechConnect World Innovation Conference and Expo, May 2018
- Kubalak, Joseph R., Wicks, Alfred L., & Williams, Christopher B. (2019). “Deposition Path Planning for Material Extrusion using Specified Orientation Fields,” In Proceedings of the 4th North American Manufacturing Research Conference
- Kubalak, Joseph R., Wicks, Alfred L., & Williams, Christopher B. (2019). “Enabling Layer-less Multi-Axis Extrusion for Printing Optimized Parts,” In Proceedings of the 30th Annual International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium


